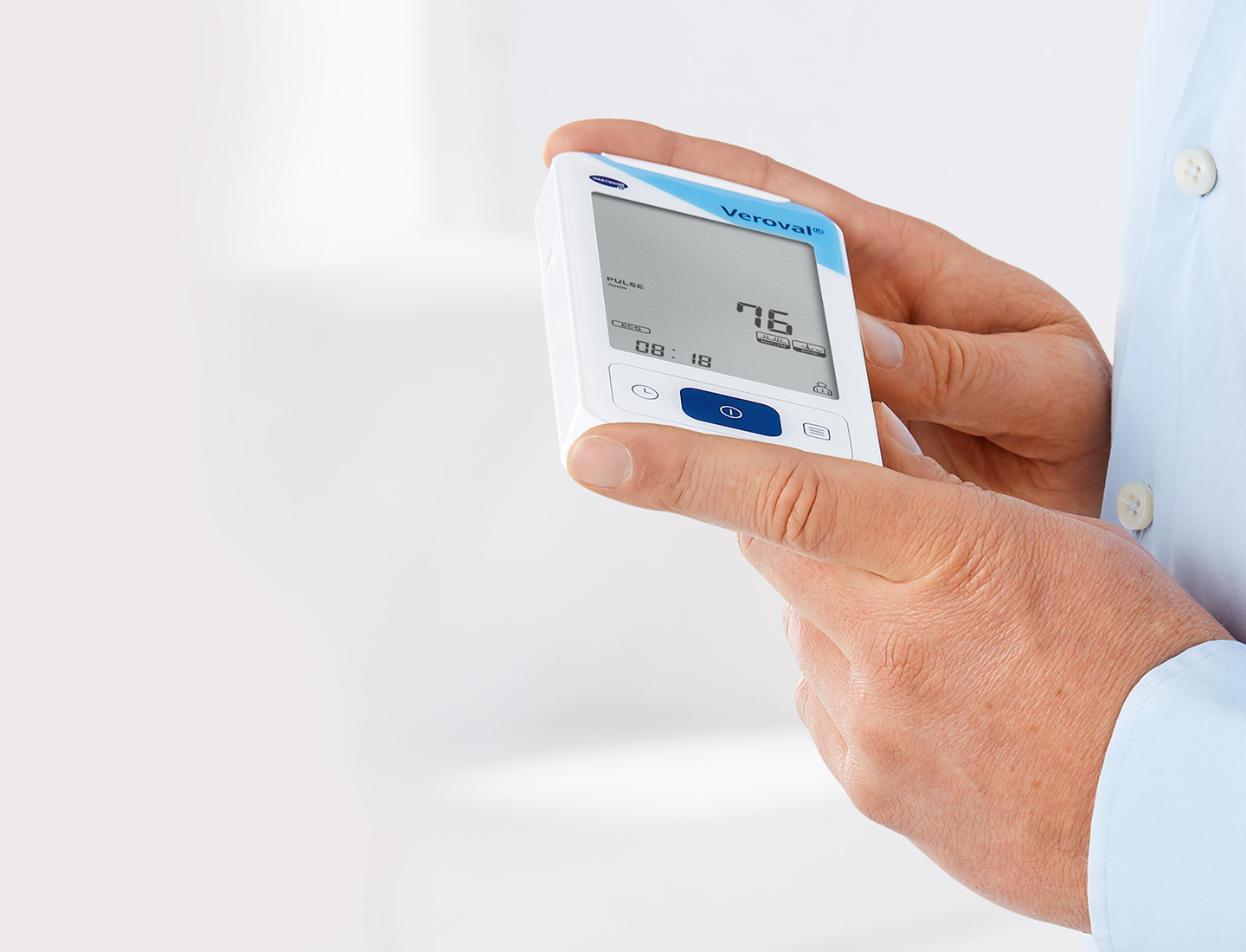
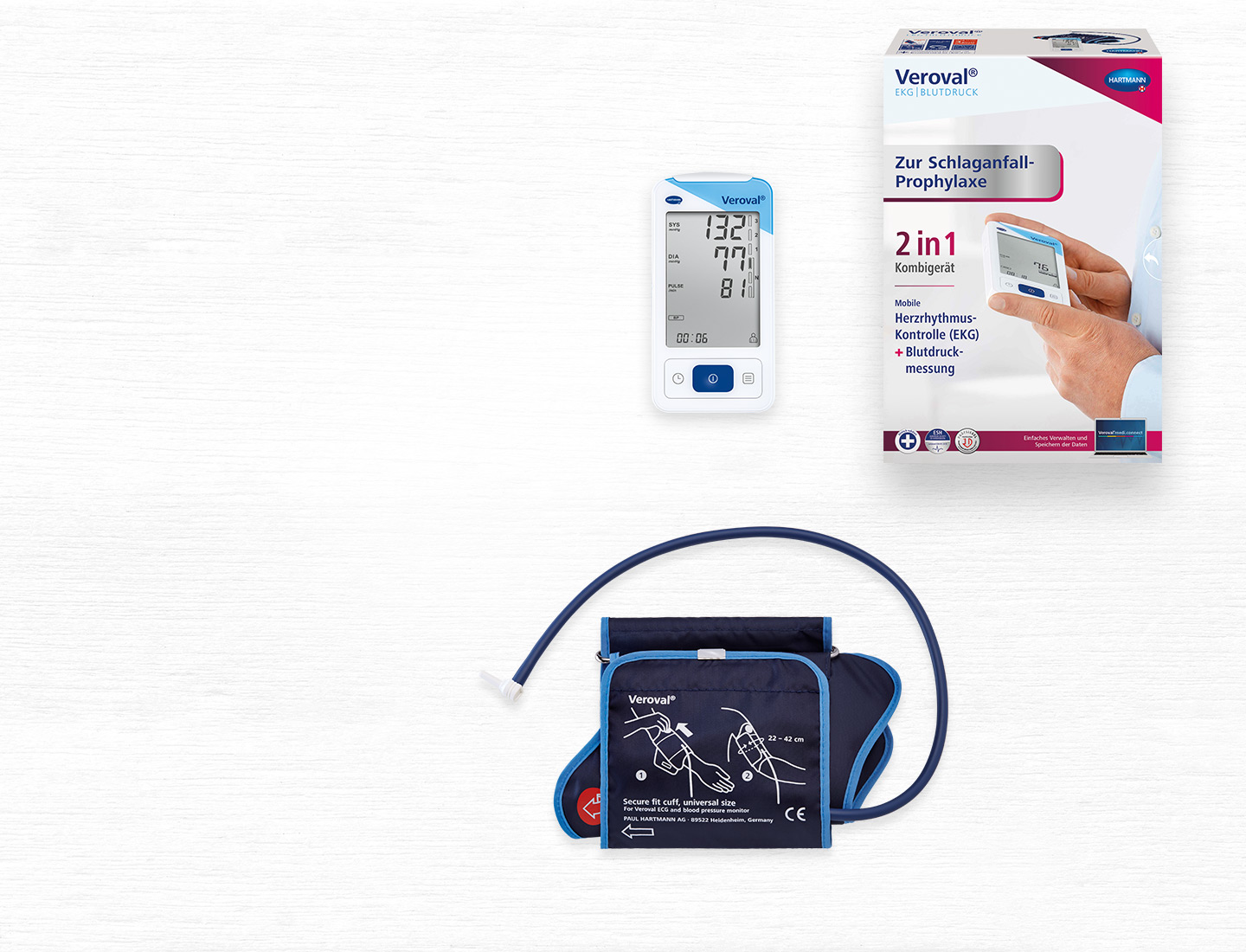
With the mobile Veroval® ECG and blood pressure combination device you can record your heart rhythm anywhere and anytime, and also measure your blood pressure.
Doubly alert for stroke prevention
2 in 1 Veroval® ECG and Blood Pressure Monitor

Knowledge
FAQ
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia and can only be detected when it occurs. It is characterized by a markedly accelerated, constantly irregular heartbeat. When atrial fibrillation occurs, the atria can no longer properly support the heart chambers during pumping. As a result, the heart does not empty completely and blood remains in the atria, where it can form clots. These clots can enter the brain and trigger a stroke.
Although atrial fibrillation is not directly life threatening, it indicates a five-fold increased stroke risk. It can therefore become life threatening if it is not recognized and treated by a doctor. Because atrial fibrillation can be asymptomatic and can only be detected when it happens, it is difficult to recognize. Patients suffering from hypertension should be cautious, as hypertensives in particular have a doubly high risk of developing atrial fibrillation, which can lead to dangerous blood clots that cause strokes.
Signs of atrial fibrillation are often unspecific, such as palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath or chest pain. Up to 30 % of the people who suffer from atrial fibrillation do not feel any symptoms at all.